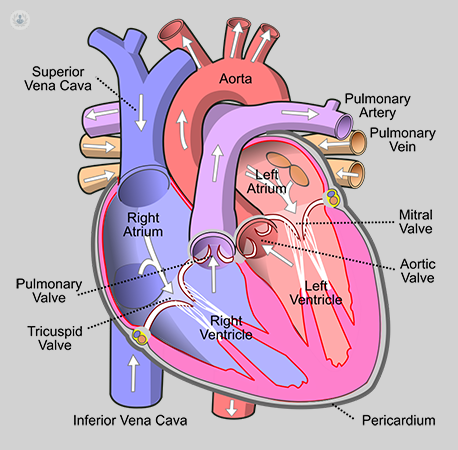
Valvular heart disease occurs when the heart valve becomes damaged or diseased. There are many causes of valve disease. A normal heart has four chambers (right and left atria, and right and left ventricles) and four valves. This can affect the flow of blood from your heart to your body. Treatment for your heart valve disease depends on the affected heart valve and the type and severity of the disease. Heart valve disease sometimes requires surgery to repair or replace the heart valve.
In valvular stenosis, the condition of valvular heart disease, the tissues that make up the valve leaflets harden, narrowing the opening of the valve and reducing the amount of blood that can flow through it. If the stenosis is mild, the overall work of the heart may not be reduced. However, the valve can become so narrow (stenotic) that the heart’s work slows down, and the rest of the body can’t get adequate blood flow. The heart is made up of 4 chambers – 2 atria (upper chambers) and 2 ventricles (lower chambers). The blood passes through a valve as it leaves each chamber of the heart. Valves prevent the backward flow of blood. They act as a one-way inlet of blood on one side of the ventricle and a one-way outlet of blood on the other side of the ventricle.
The function of heart valves
As the heart muscle contracts and relaxes, the valves open and close, allowing blood to flow into the ventricles and out to the body at alternate times. The following is a step-by-step explanation of the flow of blood through the heart.
- Once they fill with blood, the left, and right atriums contract. It opens the mitral and tricuspid valves. Then the blood is pumped into the ventricles.
- The left and right ventricles communicate. It closes the mitral and tricuspid valves preventing blood flow. At the same time, the aorta and pulmonic valves open to pump blood out of the heart.
- The left and right ventricles relax. The aortic and pulmonic valves close, preventing backward blood flow to the heart. The mitral and tricuspid valves then open to allow blood to flow back into the heart to fill the ventricles.
Causes of Valvular Heart Disease
The four valves of the heart, which keep blood flowing in the right direction, are the mitral, tricuspid, pulmonary, and aortic valves. Each valve has flaps (leaflets) that open and close once with each heartbeat. If one or more valves fail to open or close properly, the flow of blood from your heart to your body is interrupted.
Heart valve disease may occur at birth (congenital). It can also occur in adults for many reasons and conditions, such as infections and other heart conditions.
Heart valve problems include:
- Regurgitation. The valve flaps don’t close properly, causing blood to flow backward into your heart. This is usually caused by the valve flaps bulging back, a condition called prolapse.
- Stenosis. The valve flaps become thickened or hard and possibly fused together. This results in a narrow valve opening and reduced blood flow through the valve.
- An atresia valve does not form, and a solid sheet of tissue blocks the flow of blood between the heart’s chambers.
Symptoms of Valvular Heart Disease
Some people with heart valve disease may not have symptoms for years. Signs and symptoms appear may include:
- A heart murmur (heart murmur) when a doctor is listening to the heart with a stethoscope.
- Chest pain
- Abdominal swelling is more common with advanced tricuspid regurgitation.
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath especially while working or lying down.
- Swelling of your ankles and feet
- Dizziness.
- to pass out
- Irregular heartbeat
Risk factors
A number of factors can increase your risk of heart valve disease, including:
- Old age
- A history of certain infections that can affect the heart.
- A history of some form of heart disease or heart attack
- Heart conditions at birth (congenital heart disease)
Diagnosis of Valvular Heart Disease
Your doctor can perform a physical test and listen for a cardiac murmur, which may be an attainable sign of a heart valve condition. you will have many tests to diagnose your condition.
Tests could include:
- Echocardiography. Sound waves directed at your heart from a wand-like device (transducer) manufacture video pictures of your heart in motion. This takes look and evaluates the structure of your heart, the center valves, and therefore the flow of blood through your heart. the associate sonogram helps your doctor get a better check out of the center valves and the way well they’re operating. Doctors may use a 3D sonogram.
- In another sort of sonogram, referred to as a transesophageal sonogram, a tiny low electrical device hooked up to the tip of a tube is inserted down the tube leading from your mouth to your abdomen (esophagus). This takes look at helps your doctor see the center valves as closely as attainable with a daily sonogram.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG). Wires (electrodes) hooked up to pads on your skin live electrical impulses from your heart. an associate electrocardiogram will notice symptom chambers, cardiopathy, and abnormal heart rhythms.
Chest x-ray
- A chest X-ray will facilitate your doctor to verify if the center is enlarged, which may indicate bound kinds of heart valve malady. A chest X-ray may facilitate doctors to verify the condition of your lungs.
- Cardiac imaging. Internal organ imaging uses magnetic fields and radio waves to form elaborated footage of your heart. It will verify the severity of your condition and assess the dimensions and performance of your heart’s lower chambers.
- Exercise tests or stress tests. varied exercise tests facilitate live your activity tolerance and monitor your heart’s response to work up. If you cannot exercise, you will be medication that mimics the impact of exercise on your heart.
- Cardiac catheterization. This takes a look at isn’t typically accustomed to diagnose heart valve malady, however, it should be used if different tests square measure unable to diagnose or verify the severity of the condition.
A doctor threads a skinny tube (catheter) through a vessel in your arm or groin, guides it to the associate artery in your heart, and injects dye through the tube to point out au courant X-rays. Arteries square measure visible. It offers your doctor a close image of your heart’s arteries and the way your heart works. It may live the pressure within the center chambers.
Treatment of Valvular Heart Disease
Treatment for heart valve illness depends on your symptoms, the severity of the condition, and whether or not your condition is obtaining worse.
A doctor trained in cardiopathy (cardiologist) can offer your care. Treatment might embody observation of your condition with regular follow-up visits. you will be asked:
- Make healthy style changes.
- Take medication to treat symptoms.
- If you’ve got an exact irregular cardiac rhythm known as cardiac arrhythmia, take blood thinners to cut back the danger of blood clots.
Surgery or different procedures
You may eventually like heart valve surgery to repair or replace a pathologic heart valve though you do not have symptoms. If you wish surgery for an additional cardiopathy, your doctor might repair or replace the pathologic valve at a constant time.
Heart valve surgery is typically done through a cut (incision) within the chest. Doctors typically perform minimally invasive surgery, which involves smaller incisions than open surgery. In some medical centers, doctors perform robotic-assisted surgery, a kind of minimally invasive surgery within which surgeons use robotic instruments to perform the procedure.
Surgery choices embody valve repair or replacement.
Heart valve repair
Your doctor might advocate heart valve repair to preserve your heart valve. To repair a heart valve, surgeons may:
- Drill a hole within the valve.
- Separate valve leaflets that have amalgamated.
- Replace the valve support cables.
- Remove excess valve tissue therefore the valve will shut tightly.
Surgeons typically tighten or strengthen the ring around the valve (annulus) by inserting a man-made ring. In some cases, doctors use a less invasive procedure to repair sure valves mistreatment long, skinny tubes (catheters). These procedures might embody the employment of clips, plugs, or different devices.
Heart valve replacement
If the valve can not be repaires, surgeons might take away the broken valve and replace it with a mechanical valve or a valve made of cow, pig, or human heart tissue (biological or tissue valve).
If you’ve got a valve replaces with a mechanical valve, you may take blood thinners for the remainder of your life to forestall blood clots. Biological tissue valves break down over time and frequently ought to get replaces.
A minimally invasive procedure known as transcatheter semilunar valve replacement (TAVR) will be wont to replace a broken semilunar valve. during this procedure, the doctor inserts an extended, skinny tube (catheter) into AN artery in your leg or chest and guides it to a heart valve. A replacement valve is emotional to the right position through this tubing.

