Trachoma is a watch malady caused by infection with the microorganism C. trachomatis. it’s a public pathological state in forty-four countries and is accountable for visual defects or impairment in roughly one.9 million folks. visual defect from eye disease is irreversible. Trachoma
About Trachoma
Other types or strains of these bacteria can cause sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia) and disease in the lymph nodes.
This is a photomicrograph of the conjunctiva that revealed the presence of what are known as intracytoplasmic inclusions.
Trachoma is easily spread by direct personal contacts such as fingers, shared towels, and clothing, and by flies that have been in contact with the eyes or nose of an infected person. When left untreated, repeated Chlamydia trachomatis infections of the eye can cause severe scarring of the inside of the eyelid. This can cause the eyelids to scratch the cornea (trichiasis).
Chlamydia trachomatis infection spreads in areas without access to clean drinking water and sanitation systems. Globally, about 1.9 million people have vision loss due to trachoma, and it accounts for 1.4% of blindness worldwide. 1 In 2021, 136 million people lived in trachoma-affected areas and were at risk of trachoma blindness. Responsible for visual impairment. Blindness from trachoma is irreversible
Symptoms Of V
Mild itching and burning in the eyes and eyelids
Eye discharge containing mucus or pus
Swelling of the eyelids
Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
Eye pain
Redness of the eyes
Loss of vision
Young children are especially vulnerable to infection. But the disease progresses slowly, and more painful symptoms may not appear until adulthood.
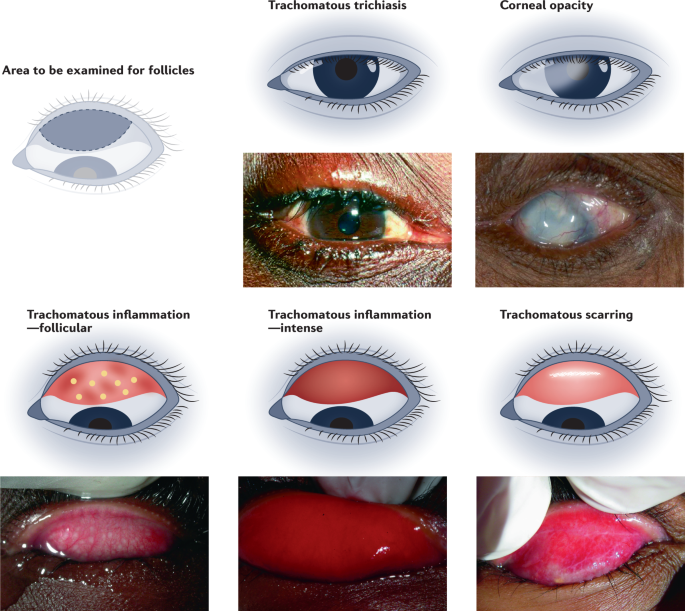
The World Health Organization (WHO) has identified five stages of trachoma development:
Inflammation – follicular. An early infection consists of five or more follicles — small bumps containing lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell — that appear enlarged on the inner surface of your upper eyelid (conjunctiva).
Inflammation – severe. In this stage, your eye is now highly infected and the upper eyelid becomes irritated with thickening or swelling.
Eyelid scars. Repeated infections lead to scarring of the inner eyelid. When examined on a large scale, scars often appear as white lines. Your eyelids may become distorted and turn into (entropion).
Alternating eyelids (trachiasis). The scarred inner layer of your eyelid continues to deteriorate, causing your eyelids to curl in such a way that they rub and scratch the clear outer surface of your eye (the cornea).
Corneal clouding (opacity). The cornea is affected by an inflammation that is commonly seen under your upper lid. Constant inflammation due to scratching from alternating eyelids leads to clouding of the cornea.
All trachoma symptoms are more severe in your upper lids than in your lower lids. Without intervention, a disease process that begins in childhood can progress into adulthood.
Prevention and Control
Eradication programs in endemic countries are being implement using the SAFE strategy recommended by the WHO. It contains:
Mass drug administration of antibiotics, particularly the antibiotic azithromycin, to clear the infection, which is donate by the manufacturer to eradication programs through the International Trachoma Initiative.
facial cleansing; And
Environmental improvements, particularly improving access to water and sanitation.
Most indigenous countries have agreed to accelerate the implementation of the strategy to achieve elimination targets.
Data reported to WHO by the Member States for 2020 show that 42,045 people with trachomatous trichiasis were provided with corrective surgery that year, and 32.8 million people in local communities were treat for trachoma eradication. It was treat with antibiotics. In 2019, when COVID-19 did not affect the capacity of community-based work programs, 92,622 people with trachomatous trichiasis were provided with corrective surgery, and 95.2 million people were treat with antibiotics.
Elimination efforts need to continue to meet the goal set by World Health Assembly Resolution WHA 51.11, which is the elimination of trachoma as a public health problem (1). The full engagement of multiple actors involved in water, sanitation, and socioeconomic development will be particularly important.
Treatment of Trachoma
Antibiotics – A single oral dose of an antibiotic (azithromycin) is the first line of treatment in uncomplicated cases. This medicine kills the bacteria so that the body’s natural healing processes can heal the eye. Antibiotics must be give to everyone in the household where trachoma is find. In areas with widespread infection, the entire community may need treatment.
Surgery – This is use to correct eyelid deformities and to reposition (turn outward) damaged eyelids in older people.
Distribution
Trachoma is hyperendemic in several of the poorest and most rural areas of the continent, Central and South America, Asia, Australia, and therefore the geographic region.
It is answerable for the cecity or vision defect of concerning one.9 million individuals. It accounts for concerning one.4% of cecity worldwide.
Overall, the continent is the most affected continent, and therefore the continent with the foremost management efforts.
As of 07 March 2022, fourteen countries had reportable achieving elimination targets. These countries are Kampuchea, China, Gambia, Ghana, Moslem Republic of Asian country, Iraq, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Mexico, Morocco, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Asian country, and African country. And Twelve of those countries – Kampuchea, China, Gambia, the Moslem Republic of Asian country, Lao People’s Democratic Republic, Ghana, Mexico, Morocco, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, and Asian country – are declare public ill health by the World Health Organization. was support as a termination.
Economic impact
The burden of eye disease on infected people and communities is gigantic. The economic price in terms of lost productivity from cecity and vision defect is calculable at US$2.9–5.3 billion annually, rising to US$8 billion once trichiasis is enclose.

