Viral diseases
Definition of viral disease
Viruses are very small infectious agents. They are made up of a piece of genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, enclosed in a coat of protein. Viruses attack your body’s cells and use the components of those cells to help them multiply. This process often damages or destroys the affected cells. A viral disease is any disease or health condition caused by a virus. Viral diseases
Viral respiratory diseases
Viral respiratory illnesses are contagious and usually affect the upper or lower part of your respiratory tract.
Common symptoms of the viral respiratory illness include:
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Cough or sneeze
- fever
- Body aches
Examples
Examples of respiratory diseases include:
- Flu
- General cold
- Respiratory syncytial virus infection
- Adenovirus infection
- parainfluenza virus infection
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS)
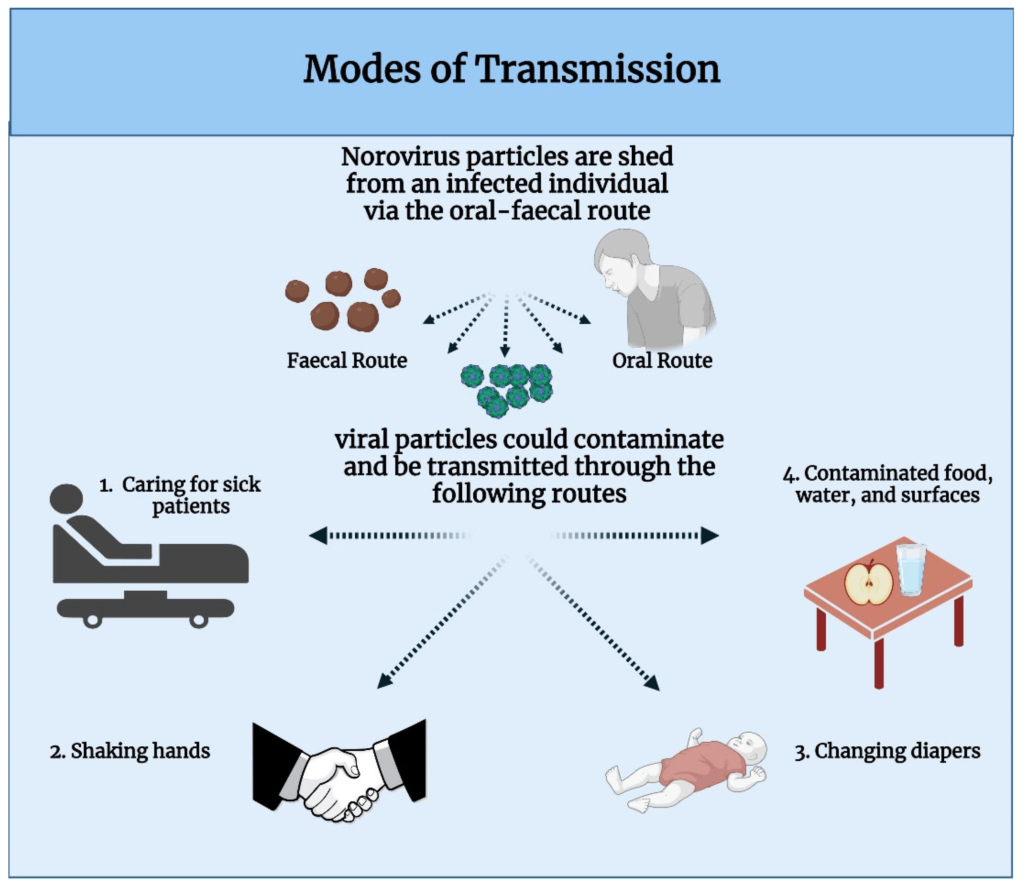
Transmission
Respiratory viruses are spread by droplets produced by coughing or sneezing. If someone with a viral illness coughs or sneezes around you and inhales the droplets, you can get the disease. The virus can also spread through contaminated objects, such as doorknobs, tabletops, and personal items. If you touch one of these things and then touch your nose or eyes, you can get sick.
Prevention
The best way to prevent viral respiratory diseases is to practice good personal hygiene. Wash your hands often, cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze, and limit your interactions with people who show symptoms of respiratory illness. There is also a vaccine that can help reduce your risk of seasonal flu.
Treatment
Viral respiratory illnesses usually resolve on their own. But over-the-counter (OTC) medications, including nasal decongestants, cough suppressants, and pain relievers, can help relieve symptoms. In addition, Tamiflu, an antiviral drug, is sometimes prescribed if a person is in the early stages of developing the flu.
Viral diseases result in a wide variety of symptoms that vary in character and severity depending on the type of viral infection and other factors, including the individual’s age and overall health. Common symptoms of viral illnesses include flu-like symptoms and restlessness.
Viral diseases are not treatable with antibiotics, which can only treat bacterial diseases and infections. However, the most common viral illnesses, the common cold, and the flu are usually self-limiting in healthy people. This means that the viral infection causes illness for a period of time, then it clears up and the symptoms go away as your immune system attacks the virus and your body heals.
In some cases, viral illnesses can lead to serious, potentially life-threatening complications, such as dehydration, bacterial pneumonia, and other secondary bacterial infections. People at risk of complications include those with a chronic illness or a suppressed or compromised immune system, and the very young and very old. In addition, some types of sexually transmitted viral infections, such as HIV/AIDS and HPV, can cause serious complications and death. Get immediate medical attention if you think you have a viral illness, especially if you are at risk of complications, or if you believe you have a sexually transmitted disease.