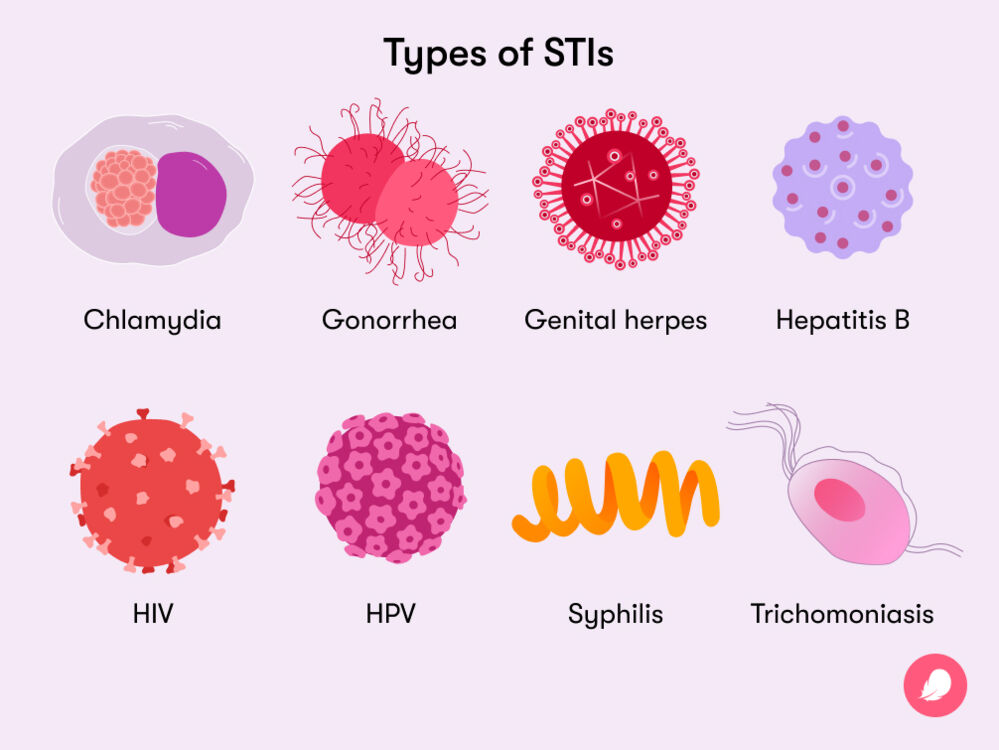
Overview
4 of these are currently treatable: syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis. There are 4 other viral infections that are incurable: hepatitis B, herpes simplex virus (HSV or herpes), HIV, and human papillomavirus (HPV). STIs are primarily spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. In 2020, WHO estimates 374 million new infections with one in four STIs: chlamydia (129 million), gonorrhea (82 million), syphilis (7.1 million), and trichomoniasis (156 million). Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
More than 490 million people were estimated to be living with genital HSV (herpes) infection in 2016, but an estimated 300 million women have an HPV infection, the leading cause of cervical cancer. An estimated 296 million people worldwide are living with chronic hepatitis B. Both HPV and hepatitis B infections can be prevent by vaccination. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are usually transmit from one person to another through sexual contact. Most are quite common, and effective treatment is available but especially in the early stages. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
How do the male reproductive organs work?
The male genital system is specialize for the subsequent functions:
To produce, maintain and transport gamete (male procreative cells) and protecting fluid (semen).
Ejaculation of gamete within the feminine procreative tract
For the assembly and secretion of male sex hormones
Male procreative anatomy includes external structures including Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- penis
- The pocket
- The testicles
- Male procreative anatomy includes internal structures including Vas deferens
- Ejaculatory ducts
- Urinary tract
- Seminal Vesicles
- Gastric secretor
- Bulbourethral Gland (Cowper’s Gland)
STI symptoms
- An abnormal discharge from the canal, penis, or anus
- Pain whereas urinating
- A lump or skin growth around the private parts or bottom (anus).
- A rash
- Abnormal channel hemorrhage
- Itchy private parts or opening
- Blisters and sores around your private parts or opening
- Warts around your private parts or opening
- Warts in your mouth or throat, however, can be rare.
Diagnosis of STIs
Accurate diagnostic tests for STIs are units widely utilized in high-income countries. they’re notably helpful for the diagnosis of symptomless infections. However, diagnostic tests area unit for the most part unprocurable in low- and middle-income countries so wherever testing is offer, it’s typically costly and geographically inaccessible, and patients so typically have to be compell to wait a protracted time (or got to return) to induce results. As a resultso follow-up is also interrupt but care or treatment is also incomplete.
The only low-cost, speedy tests presently out there for STIs area unit Cupid’s disease, viral hepatitis and HIV. The speedy Cupid’s disease take a look at is already in use in some resource-limited settings. A speedy twin HIV/syphilis take a look at is currently out there that permits an individual to check for HIV and Cupid’s disease with a fingerstick and employing a single testing cartridge so These tests area unit correct, will give leads to fifteen to twenty minutes, and area unit straightforward to use with minimal coaching. speedy Cupid’s disease tests are shown to extend the amount of pregnant ladies being test for Cupid’s disease. However, redoubled efforts in area units are still require in most low- and middle-income countries to confirm that every one pregnant ladies area unit tested for Cupid’s disease at their initial antepartum care visit.
Several speedy tests for different STIs area unit below development and have the potential to enhance STI diagnosing and treatment, notably in resource-limited settings.
Treatment of Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
Effective treatments are currently available for a number of STIs.
Three bacterial STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea and syphilis) and one parasitic STI (trichomoniasis) are usually treatable with the current single dose of antibiotics.
For herpes and HIV, the most effective drugs available are antivirals so which can alter the course of the disease, although they cannot cure the disease.
For hepatitis B, antiviral medications can help fight the virus and slow liver damage.
The Gonococcal AMR Surveillance Program (GASP) has shown high rates of resistance to many antibiotics so including quinolone resistance, increasing resistance to azithromycin and emerging resistance to extended-spectrum cephalosporins, a last-line treatment. Increases the risk that gonorrhea will be untreatable (4).
AMR for other STIs, although less common, also exists, making prevention and prompt treatment important.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) Case management
Low- and middle-income countries rely on the identification of consistent, easily recognizable signs and symptoms to guide treatment, without the use of laboratory tests. This is call syndromic management. This approach, which often relies on clinical algorithms, allows health workers to diagnose specific infections based on observed syndromes (eg, vaginal discharge, urethral discharge). discharge, genital ulcers, abdominal pain).
Syndromic management is simple, assures rapid, same-day treatment, and avoids expensive or unavailable diagnostic tests for symptomatic patients but This approach results in overtreatment and missed treatment but the majority of STIs are asymptomatic. Thus, WHO recommends that countries improve so syndromic management gradually. Additionally, STI screening strategies are important for those at high risks but such as sex workers, men who have sex with men but adolescents in some settings, and pregnant so women with potentially serious consequences. because.
To prevent transmission of infection and prevent reinfection, treatment of sexual partners is an important component of STI case management.
Behavior change is complex
Despite considerable effort to identify simple interventions so that reduce risky sexual behavior so behavior change remains a complex challenge but Research has demonstrated the need to focus on carefully defined populations, consult extensively with identified target populations, and involve them in design, implementation, and evaluation.
Education and counseling can improve people’s ability to recognize STI symptoms and increase the likelihood that they will care for and encourage a sexual partner so Unfortunately, lack of public awareness, lack of training among health workers, and long-standing stigma surrounding STIs are barriers to greater and more effective use of these interventions.

